درک انواع مختلف نیروها و تأثیر آنها بر مصالح و سازه ها برای مهندسین و طراحان برای اطمینان از ایمنی و کارایی در ساخت و بهره برداری از پروژه های مهندسی مختلف ضروری است.
بیایید هر نوع نیرو را توضیح دهیم:
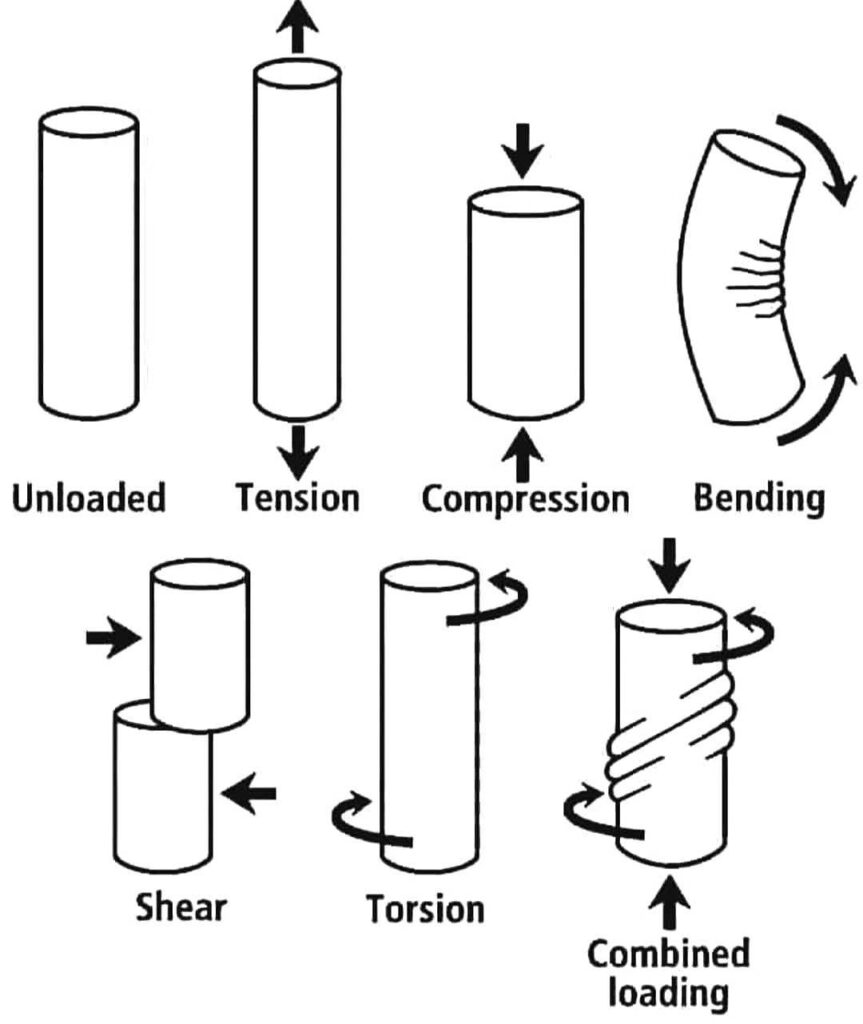
- تنش (Tension)
کشش نیرویی است که تمایل به کشیده شدن یا کشش یک جسم دارد. زمانی اتفاق می افتد که دو نیرو در امتداد یک خط مستقیم از یکدیگر دور شوند. کشش مسئول جدا کردن مواد است و معمولاً در سازه هایی مانند کابل ها، طناب ها و فنرها مشاهده می شود. - فشرده سازی (Compression)
فشرده سازی نیرویی است که تمایل دارد یک جسم را کوتاه یا له کند. زمانی اتفاق می افتد که دو نیرو در امتداد یک خط مستقیم به سمت یکدیگر وارد شوند. فشرده سازی مسئول هل دادن مواد به یکدیگر است و معمولاً در ستون ها، تیرها و سایر عناصر باربر مشاهده می شود. - خم شدن (Bending)
خمش ترکیبی از کشش و فشار است که باعث میشود یک جسم، معمولاً یک تیر یا یک عضو ساختاری، تنشهای داخلی را تجربه کند که مناطق مقعر و محدب ایجاد میکند. زمانی اتفاق می افتد که یک نیروی خارجی عمود بر محور طولی جسم اعمال شود. خمش در طراحی پل ها، ساختمان ها و سایر سازه ها بسیار مهم است. - برش (Shear)
برش نیرویی است که باعث می شود یک لایه ماده از روی لایه دیگر در امتداد یک صفحه موازی بلغزد. زمانی اتفاق میافتد که دو نیرو در جهت مخالف، موازی یکدیگر، اما نه در امتداد یک خط، عمل کنند. نیروهای برشی در پیچها، پرچها و سایر بستهایی که مواد را در کنار هم نگه میدارند، رایج است. - پیچ خوردگی (Torsion)
پیچش نیرویی است که باعث می شود جسم در امتداد محور طولی خود بپیچد. زمانی اتفاق می افتد که نیروها در جهت مخالف عمل کرده و باعث حرکت پیچشی می شوند. نیروهای پیچشی در شفت ها، پروانه ها و سایر اجزای دوار قابل توجه است. - بارگذاری ترکیبی (Combined Loading)
بارگذاری ترکیبی شامل اعمال همزمان نیروهای متعدد بر یک سازه است. این نیروها می توانند کشش، فشار، خمش، برش و پیچش را ترکیب کنند. در سناریوهای دنیای واقعی، سازه ها اغلب تحت بارهای مختلفی قرار می گیرند و مهندسان برای اطمینان از یکپارچگی سازه باید تمام این نیروها را در هنگام طراحی در نظر بگیرند.
نسخه اصلي
Understanding the different types of forces and their effects on materials and structures is fundamental for engineers and designers to ensure safety and efficiency in the construction and operation of various engineering projects.
Let’s describe each type of force:
+ Tension:
Tension is a force that tends to elongate or stretch an object. It occurs when two forces act away from each other along the same straight line. Tension is responsible for pulling materials apart and is typically observed in structures like cables, ropes, and springs.
+ Compression:
Compression is a force that tends to shorten or squash an object. It occurs when two forces act towards each other along the same straight line. Compression is responsible for pushing materials together and is commonly observed in columns, beams, and other load-bearing elements.
+ Bending:
Bending is a combination of tension and compression that causes an object, usually a beam or a structural member, to experience internal stresses that create concave and convex regions. It happens when an external force is applied perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the object. Bending is crucial in the design of bridges, buildings, and other structures.
+ Shear:
Shear is a force that causes one material layer to slide past another layer along a parallel plane. It occurs when two forces act in opposite directions, parallel to each other, but not along the same line. Shear forces are common in bolts, rivets, and other fasteners that hold materials together.
+ Torsion:
Torsion is a force that causes an object to twist along its longitudinal axis. It occurs when forces act in opposite directions, causing a twisting motion. Torsional forces are significant in shafts, propellers, and other rotating components.
+ Combined Loading:
Combined loading involves the simultaneous application of multiple forces on a structure. These forces can combine tension, compression, bending, shear, and torsion. In real-world scenarios, structures are often subject to various loads, and engineers need to consider all these forces when designing to ensure structural integrity.
 مدرسه تاسیسات آموزش تاسیسات مکانیکی و الکتریکی ساختمان
مدرسه تاسیسات آموزش تاسیسات مکانیکی و الکتریکی ساختمان